This is a sponsored message.
Global Disruptions, Health Equity, and Data Sharing
International clinical trials are essential to evaluating the safety and efficacy of new treatments, but their success can be hampered by a variety of challenges. A recent McKinsey analysis of drugs and vaccines developed since 2000 shows that it takes nearly 10 years to go from clinical testing to approval. Additionally, how do you ensure that the vaccine distribution is equitable?
When time is of the essence, how do you scale trials internationally for success? First, let’s look at some challenges and then opportunities.
Data Sharing Beyond Borders
One of the most difficult aspects is sharing data between countries – especially when it comes to patient health information, which must remain secure while navigating a variety of different laws.
Another challenge faced by international clinical trials is the lack of reliable data about local health systems and regulations. Many countries have laws that govern how a trial must be conducted, making it difficult for pharma and biotech companies to navigate without local knowledge.
Using artificial intelligence (AI), especially Generative AI, and predictive analytics, companies can access reliable datasets, allowing informed decisions about where to conduct research without needing onsite visits or relying on outdated resources.
Additionally, clinical trials are no longer confined to one country or region. With the globalization of drug development, clinical operations and feasibility teams are now tasked with navigating the complexities of international data sharing for their clinical studies. From legal considerations to data privacy regulations, the challenges facing these teams can be daunting.
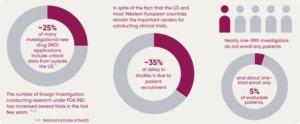
Pharma and biotech companies already face significant challenges in conducting international clinical trials. From natural disasters, war, cultural differences, and regulations to language barriers and data privacy issues, the complexity of coordinating multiple countries can be overwhelming.
For each country involved, there are different laws and regulations governing data sharing – including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, and various other laws around the world.
To complicate matters further, there are often differences in language, culture, and communication protocols between countries. This makes it more difficult to ensure accurate data sharing between sites since misunderstandings can occur easily.
Some countries may have difficulty accessing or utilizing certain technologies due to outdated infrastructure or lack of resources. All of these factors make international data sharing even more challenging for clinical operations teams.
Global Disruptions
In early 2022, the invasion of Ukraine by Russia had devastating consequences – for Ukraine, Russia, neighboring countries, and the world at large. Catastrophes also impact scientific and medical progress and have a profound impact on all of us. Science and medicine have no borders, but sudden, unanticipated disruptions to medical testing and clinical trials impede progress toward new breakthroughs and new therapies that millions of patients around the world hang their hopes on.
The disruption to these trials had a ripple effect not just for Ukraine, but for the entire global healthcare ecosystem and millions of patients and their families around the world. Ukraine and many neighboring countries were and still are relying on these clinical trials to bring new and improved medicine, treatments, and technology to healthcare.
It is clearer than ever that we need a new, agile response to global clinical trial disruptions to preserve progress, ensure continuity and provide patients with the treatments they depend on.
Patient Recruitment
One of the main barriers to efficient and successful international clinical trials is the difficulty in recruiting enough patients to conduct meaningful research.
By using predictive analytics and data-driven solutions, pharma and biotech companies can tap into large databases of patient data that can be used to identify potential participants who meet the criteria needed for a given trial. This not only saves time in recruitment, but also helps to ensure that trials include more diverse populations who may respond differently to treatments than those typically found in localized studies.
Finally, some countries lack the infrastructure necessary for successful clinical trials due to limited financial resources or access to skilled personnel. By leveraging predictive analytics and data-driven solutions, companies can identify underperforming sites before starting a trial with the goal of ensuring timely completion with quality results. Companies can use this information to select sites that have higher success rates or provide more resources if needed.
With its ability to quickly assess risk factors associated with trial success while taking into account local health systems and regulations, predictive analytics offers an unprecedented level of efficiency when planning international clinical trials that could save both time and money while helping reach more diverse patient populations faster than ever before.
Use Case: Site Feasibility
When evaluating prospective sites for a clinical trial, it’s important to consider the following factors: location (both in and outside the U.S.), size and expertise of staff, patient demographics, infrastructure, and access to specialized technology.
Data analytics and insights platforms like H1 can help streamline the process of evaluating and comparing sites by providing real-time access to site information. These tools can also be used to analyze data more efficiently, allowing investigators to make informed decisions quickly.
One of H1’s clients leveraged our Trial Landscape clinical trial intelligence solution and took a data-driven approach. Trial Landscape helped the company find key strategies, data insights, and analytics for optimizing the site feasibility process and ensuring successful clinical trials in novel therapies. Read the case study to learn more.
Overall, international data sharing for clinical trials doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By taking advantage of technology platforms as well as adopting standardized protocols across sites involved in a trial, feasibility teams can reduce their risks while still ensuring compliance with global regulations related to patient health information security and privacy laws like GDPR and HIPAA. With a little extra effort upfront during the planning stages of a trial, organizations can help streamline processes and increase the overall success rates of their international studies without compromising on safety or security measures.
Request a demo of Trial Landscape.



